Fueling the nation
Enabling green energy access across the country will provide us with a clean, safe, cheaper and convenient alternative source
With a population of 1.3 billion, India is the second most populated country in the world with a projected increase in energy demand of 165 per cent by 2040, nearly three times the growth projected for the non-OECD countries combined. Ensuring access to safe, reliable and clean energy is a growing challenge for the country
Natural gas has played an important role in India's energy supply mix. Natural gas is critical for fertiliser and power generation in India and it is also important for other sectors such as petroleum refining, petrochemicals, manufacturing and city gas distribution. As India achieves its baseline targets of universal access to electricity and clean cooking fuel, it faces the challenge of balancing air quality, health, climate and energy security concerns with the need for affordable energy. The Government has a stated objective of increasing the use of natural gas from the current 6 per cent to 15 per cent by 2030. The Government of India has envisaged a cleaner, greener and more inclusive future for India by placing "accelerating our efforts to move towards gas-based economy" at top of the seven elements of India's energy sector vision.
India has focused on increasing natural gas in its national energy supply mix and expansion of its gas pipeline infrastructure. With recent expansions in the distribution networks, it is expected that over 70 per cent of the population will have access to natural gas by 2023, an impressive increase from a decade ago when only 10 per cent of the population had access to natural gas. India has nearly 17,900 km of natural gas pipeline in operation, with a further 16,600 km approved, or under construction. Government has been hand holding a lot of these projects in a focussed way to complete the required infrastructure to meet its vision.
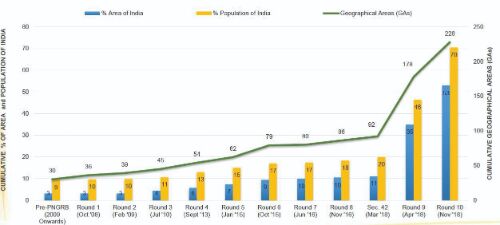
Until 2014, only 34 Geographical Areas (GAs) had been awarded in total for development of City Gas Distribution networks in the country indicating a slow pace of CGD infrastructure growth. After the latest Round 10, coverage of CGD network has been expanded to 232 GAs, spread over 407 districts across 27 States/UTs. It has the potential to make gas accessible to 70 per cent of the country's population.
As of October 31, 2020, there were around 70 lakh domestic household connections and around 2,436 CNG stations in the country. The investment across the CGD sector is estimated to be around INR 90,000 crore in the next 5-7 years.
This will lead to direct and indirect employment generation for around 3.5-4 lakh people across India. It would also facilitate access to clean and affordable energy to over four crore households by 2027.
It is one of the cleanest burning transportation fuels in the market today. CNG is amongst the green fuels as it reduces harmful emissions because of Lead and Sulphur free character. CNG produces the least emissions of all other fuels and contains significantly lesser pollutants than conventional liquid fuels. It produces 20-30 per cent lesser greenhouse gas emissions and 95 per cent lesser tailpipe emissions than petroleum products. Since CNG fuel systems are completely sealed, CNG run vehicles produce no evaporative emissions. Further, being non-corrosive, it enhances the longevity of spark plugs as well. Due to the absence of any lead or benzene content in CNG, the lead fouling of spark plugs, and lead or benzene pollution are eliminated.
India currently has around 3.3 million CNG vehicles running on roads but they are primarily concentrated in Western India due to the infrastructure availability. At the end of December 2020, there were 2,436 CNG stations in India and 82 per cent of the total CNG stations were located in Delhi, Mumbai and Gujarat. As India is planning a rollout of 10,000 CNG gas stations in a decade under its CGD expansion programme, it is expected that the share of CNG based vehicles will rise over the years due to cost advantage and focus on urban pollution. This will bring significant savings for Indian citizens as CNG is cheaper by 60 per cent and 45 per cent respectively as compared to petrol and diesel while Piped Natural Gas (PNG) is cheaper by 40 per cent than market priced LPG. Interestingly, as the CNG infrastructure improves across India, some of the major vehicle makers are looking at developing pure CNG vehicles as part of their future expansion plan.
Investment in natural gas infrastructure has provided urban dwellers with a clean, safe, cheaper and convenient alternative source of fuel for cooking for households previously reliant only on LPG. Thereby, enabling us to dream of a better tomorrow for us and the generations to come.
The writer is Director (Business Development) GAIL (India) Limited. Views expressed are personal



